Correlation Between Serum Vitamin D Levels and the Severity of Androgenetic Alopecia
19 Aug, 21
Introduction
Vitamin D deficiency has been hypothesized to play a role in various hair disorders like male and female pattern hair loss and alopecia areata.
Aim
To evaluate the levels of vitamin D in patients with androgenetic alopecia (AGA), and also to determine its possible role in the etiopathogenesis of male androgenetic alopecia.
Patient Profile
Males aged less than or equal to 30 years with a clinical diagnosis of androgenetic alopecia
Methods
- Hospital-based case–control study
- Clinical diagnosis of androgenetic alopecia
- A venous blood sample was taken from all the cases and controls, and their serum vitamin D levels were measured by the radioimmunoassay technique
- The values were interpreted as follows
- <30 nmol/L: deficient
- 31–50 nmol/L: insufficient
- >50 nmol/L: sufficient
- >150 ng/mL: intoxication
Results
- The maximum number of cases had grade V androgenetic alopecia (35%), followed by grade IV (33%), grade III (25%), and grade VI (7%)
- The mean levels of serum vitamin D were significantly decreased in cases compared to controls (20.10 vs. 29.34 ng/ mL; P ≤ 0.001)
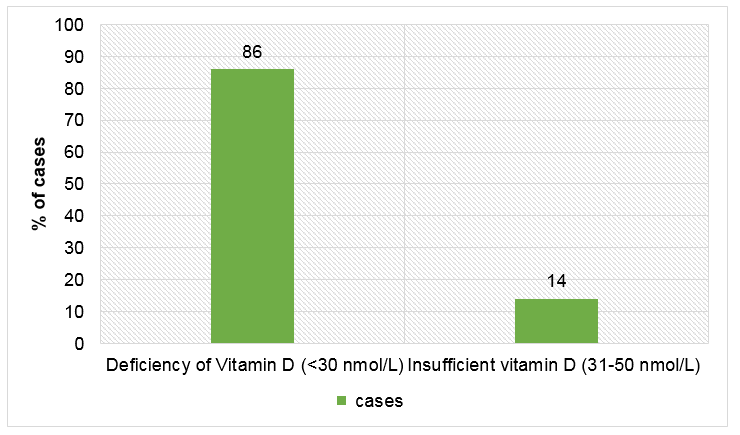
- Eighty six percent of the cases had deficiency of vitamin D (<30 nmol/L), while 14% had insufficient vitamin D levels (31-50 nmol/L)
- A statistically significant
apositive correlation between vitamin D deficiency and severity of AGA was observed
Table 1: Serum vitamin D levels and average daily sun exposure (hours) between the cases and controls
|
|
Cases (n = 50) |
Control (n = 50) |
P value |
|
BMI |
23.9 + 3.6 |
22.4 + 2.4 |
0.06 |
|
Serum vitamin D levels |
20.10 + 4.8 |
29.34 + 5.6 |
<0.001 |
|
Average sun exposure(hours) |
2.36 + 1.2 |
3.23 + 1.6 |
0.98 |
Figure 1: Mean levels of serum vitamin D in cases
- No correlation seen with duration of sun exposure serum vitamin D levels (P value = 0.98).
- 2.36 + 1.2 in cases
- 3.23 + 1.6 in controls
Conclusion
- The study demonstrated a significant correlation between vitamin D deficiency and the severity of androgenetic alopecia
- The findings indicate that vitamin D may play a role in the premature onset of androgenetic alopecia
- Hence, vitamin D levels should be assessed in AGA patients
Reference
Int J Dermatol 2020;59;9:1113-1116.

.svg?iar=0&updated=20230109065058&hash=B8F025B8AA9A24E727DBB30EAED272C8)