Introduction
Otitis externa is accompanied by severe diffuse edema of the cartilaginous part of the external auditory canal skin, which makes the use of topical antibacterial drugs challenging. Ciprofloxacin is a drug of choice for treating severe otitis externa. It exerts a bactericidal effect on gram-negative microorganisms not only during division but also at the resting stage. Limited research is conducted in the primary care environment over the use of topical or oral antibiotics therapy in otitis externa management.
Aim
To evaluate the clinical and microbiological efficacy and safety profile with oral ciprofloxacin in the external bacterial otitis (EBO) management.
Patients Profile
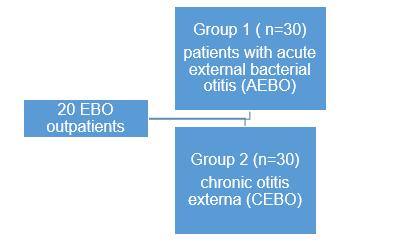
- N=60
- Patients of both genders (male ;n=24 and female; n=36)
- 1 9 to 60 years (median age 34.7 + 5.6 years)
- EBO symptoms during the acute stage or during the exacerbation stage of chronic otitis externa
|
|
Absent |
Mild |
Moderate |
Severe |
|
|
Complaints by patients |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ear pain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AEBO (Group 1) (N =30) n (%) |
0 (0%) |
0 (0%) |
0 (0%) |
30 (100%) |
|
|
CEBO (Group 2) (N = 30) n (%) |
0 (0%) |
0 (0%) |
0 (0%) |
30 (100%) |
|
|
Hearing Impairment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
2 (7%) |
4 (13%) |
5 (16%) |
19(63%) |
|
|
Group 2 |
5(16%) |
4(13%) |
16 (53%) |
5 (16%) |
|
|
Ear Discharge |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
0 (0%) |
1 (3%) |
4 (13%) |
25(83%) |
|
|
Group 2 |
0 (0%) |
2 (7%) |
23 (77%) |
5 (16%) |
|
|
Skin Itching |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
0 (0%) |
0 (0%) |
1 (3%) |
29 |
|
|
Group 2 |
0 (0%) |
1 (3%) |
1 (3%) |
28 |
|
|
Tragus Symptom |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
0 (0%) |
0 (0%) |
3 (10%) |
27(90%) |
|
|
Group 2 |
0 (0%) |
8 (27%) |
7 (2 3%) |
15(50%) |
|
|
Increase in Body Temperature |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
3 (10%) |
3(10%) |
23 (77%) |
1 (3%) |
|
|
Group 2 |
6(20%) |
6 (20%) |
18 (60%) |
0 (0%) |
|
|
Otoscopy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Flushing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
0 (0%) |
0 (0%) |
0(0%) |
30(100%) |
|
|
Group 2 |
0(0%) |
0(0%) |
0(0%) |
30(100%) |
|
|
Infiltration |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
0(0%) |
0(0%) |
0(0%) |
30(100%) |
|
|
Group 2 |
0(0%) |
0(0%) |
0(0%) |
30(100%) |
|
|
EACO narrowing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
0 (0%) |
2 (7%) |
3(10%) |
25 (83%) |
|
|
Group 2 |
0 (0%) |
4 (14%) |
5 (16%) |
21(70%) |
|
|
Difficult microscopic examination |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Group 1 |
0 (0%) |
0 (0%) |
2 (7%) |
28 (94%) |
|
|
Group 2 |
0 (0%) |
2 (7%) |
2 (7%) |
26 (87%) |
|
Methods
- Prospective observational study
- Conducted at Otorhinolaryngology center in Moscow
Study Treatment
- In each group, patients received Ciprofloxacin 500 mg twice daily with standard topical EBO treatment for up to 10 days
- Patients underwent evaluation on study visit days 1, 3, 5, and 10 for the severity. Bacteriological examination of ear canal cultures took place on Day 1 and Day 10.
Study Endpoints
- Clinical Effectiveness: The proportion of patients who experienced clinical success as assessed by complete resolution of the inflammatory process at the end of therapy in both the groups.
- Antimicrobial Effectiveness: The bacteriological eradication at the end of therapy
Results
Clinical Effectiveness
- Positive dynamics on otoscopy and complete resolution of the inflammatory process in the external auditory canal by the end of therapy
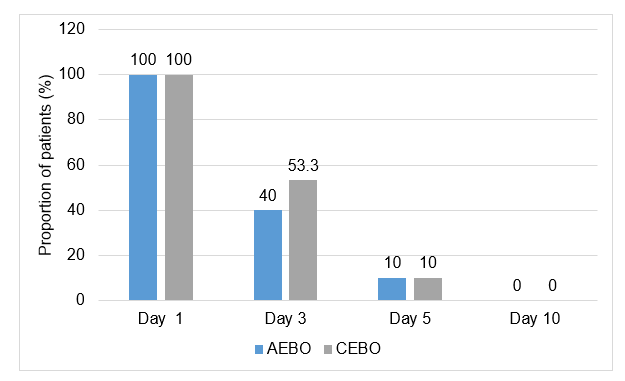
- Overall, the narrowing as observed by otoscopy on day 5 persisted in
Group 1= 12 (40%) patients
Group 2= 13 (43%) patients
- Positive dynamics and complete resolution was reported for other signs and symptoms such as ear discharge skin itching, tragus symptom (high tenderness while pressing tragus), increase in body temperature flushing and skin infiltration, and difficult microscopic examination were also present in patients from baseline to Day 10 in both groups.
|
|
AEBO |
CEBO |
|
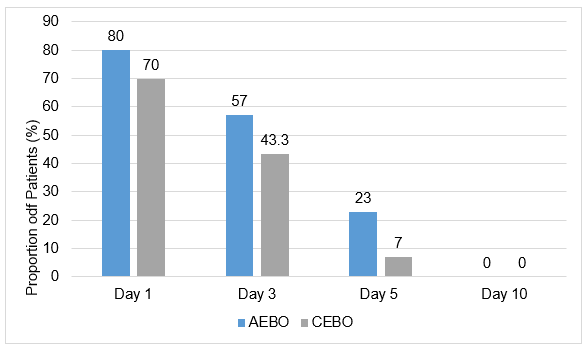
Ear Discharge |
||
|
Day 1 |
97 |
93 |
|
Day 3 |
93 |
90 |
|
Day 5 |
23 |
13 |
|
Day 10 |
0 |
0 |
|
Body Temperature |
||
|
|
AEBO |
CEBO |
|
<37.0 deg |
|
|
|
Day 1 |
10 |
20 |
|
Day 3 |
20 |
23 |
|
Day 5 |
33.3 |
30 |
|
Day 10 |
0 |
0 |
|
37.4-37 deg |
|
|
|
Day 1 |
77 |
60 |
|
Day 3 |
63.3 |
46.6 |
|
Day 5 |
13.3 |
30 |
|
Day 10 |
0 |
0 |
|
>37.5 deg |
|
|
|
Day 1 |
33.0 |
0 |
|
Day 3 |
0 |
0 |
|
Day 5 |
0 |
0 |
|
Day 10 |
0 |
0 |
Microbial Effectiveness
- On Day 10, 5 patients in Group 2 and 3 patients in Group 1 revealed the presence of S. epidermidis on microbial culture, which should be regarded as saprophytic flora
- However, 2 patients in Group 2 revealed S. aureus and Klebsiella spp. in their microbial culture
- Swimming was the major risk factor associated with the disease in addition to the most common pathogenic organisms - Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Safety
- No drug-associated adverse events and side effects in patients during the treatment
Conclusion
- Oral Ciprofloxacin 500 mg twice daily for 7 to 10 days demonstrated clinical and microbiological efficacy in the treatment of otitis externa
- It was comparatively safer than other antimicrobials
- The findings indicate that oral ciprofloxacin 500 mg twice daily for 7 to 10 days may be prescribed on a routine basis, particularly in severe cases or in high-risk patients suffering from diabetes or immune suppression
Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2017;21:329–335.