Understanding Parkinson Disease
11 Aug, 18
What is Parkinson’s disease?
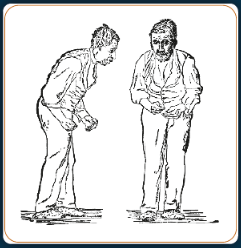
- Parkinson’s disease is a brain disorder in which movement of the body is affected.
- A person with Parkinson’s disease experiences slow body movements, stiff hands and legs, problems with balance and coordination, walking, etc.
- As the disease progresses, the person is unable to move and carry out daily living activities.
What causes Parkinson’s disease?
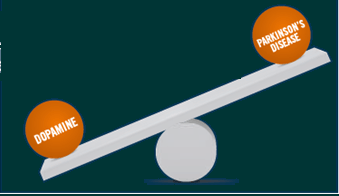
- Imbalance in brain chemicals - A brain chemical called dopamine responsible for normal motor function is reduced in Parkinson’s disease.
- Genetic factors
- Environmental factors
Who can get Parkinson’s disease?
Usually develops after age of 50. However, there have also been cases of people getting PD at the age of 40-45.
What are the clinical features of Parkinson’s disease?
- Tremors or shaking of the hand, arm or leg when awake and sitting or standing but disappears when that body part is moved
- Rigidity or stiffness in arms or legs which can be painful
- Slow or limited movement e.g. hard to get out of a chair or turn over in bed
- Poor balance and coordination e.g. sudden freezing of legs and falling
What are the other important signs and symptoms of Parkinson’s disease?
- Decreased facial expression
- Problems with swallowing which can cause drooling and choking
- Problems with speech
- Sleep disturbances
- Emotional changes
- Urinary problems and constipation
- Depression
Progression of Parkinson’s Disease with Time
- One side of the body is affected with mild symptoms.
- Both sides are affected. Symptoms become worse.
- Loss of balance and falls are common.
- Unable to stand without assistance, movement requires walking-aid.
- Bed-ridden or wheel chair bound.
Treatment and Management of Parkinson’s Disease
Medications
- There are many medications available to control the symptoms, effectively and to improve everyday functioning.
Exercise
Exercise improves
- Muscle tone
- Strength
- Flexibility
- Movement
A Healthy Lifestyle
- Follow a well-balanced, healthy and nutritious diet
- Increase water and/or fluid intake
- Avoid alcohol, caffeine, nicotine, etc.
- Develop sleep routine for good quality sleep
Manage Stress through Relaxation Techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing
Stay Connected to your Loved Ones
References
- Understanding Parkinson’s disease, 2012. American Academy of Neurology.
http://patients.aan.com/globals/axon/assets/10024.pdf (accessed on March 15, 2016)
- Understanding Parkinson’s. Parkinson’s Foundation.
http://www.parkinson.org/Understanding-Parkinsons (accessed on March 15, 2016)
- Parkinson’s disease guide. https://www.webmd.com/parkinsons-disease/guide/ (accessed on March 15, 2016)
- PD library. Parkinson’s Foundation. http://parkinson.org/pd-library (accessed on March 15, 2016)