DESIROX (deferasirox) is indicated for the treatment of chronic iron overload due to blood transfusions (transfusional hemosiderosis) in patients 2 years of age and older.
Desirox (Deferasirox): Information for the Physician
12 Oct, 11
Information for the Physician
Indications
When to Initiate Therapy
- When a patient has evidence of chronic iron overload (e.g. transfusion of approximately 100 mL/kg of packed RBCs (approximately 20 units for a 40 kg patient), and
- Serum ferritin is consistently >1000 mcg/L. the nsk for toxicity may be increased when deferasirox is given to patients with low iron burden or with serum ferritin levels that are only slightly elevated.
Starting Dose
- The recommended initial daily dose is 20 mg/kg body weight.
Dose Modifications
DESIROX may require dose adjustment, interruption or cessation of therapy due to toxicity or any of the following
Based on Serum Ferritin
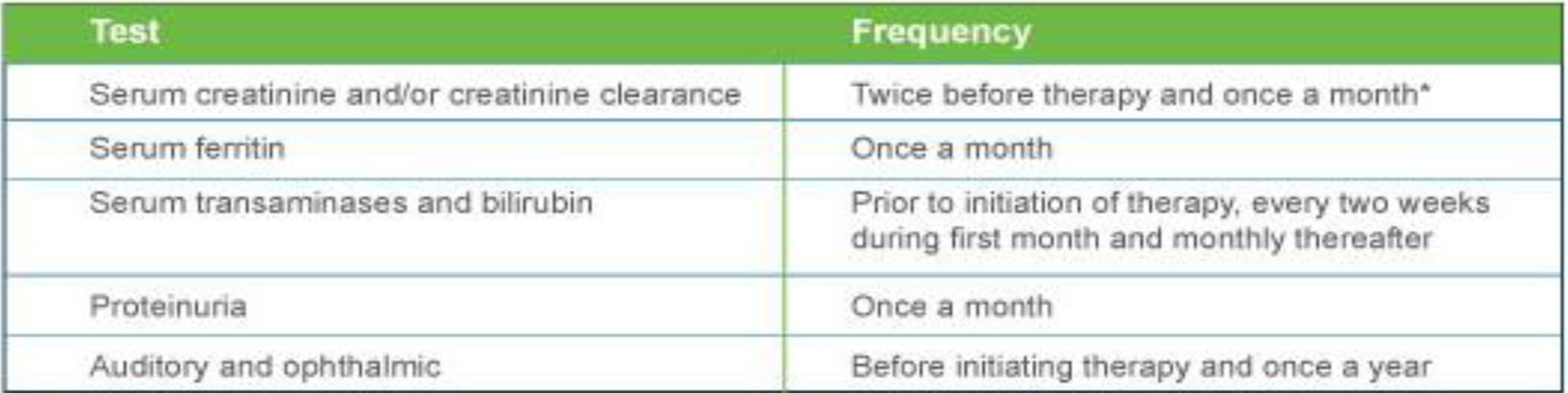
- After commencing initial therapy, monitor serum ferritin every month and adjust the dose if necessary every 3-6 months based on serum ferritin trends.
- Make dose adjustments in steps of 5 or 10 mg/kg and tailor adjuments to the individual patient's response and therapeutic goals (maintenance or reduction of body iron burden).
- In patients not adequately controlled with doses of 30 mg/kg (e g , serum ferritin levels persistently above 2500 mcg/L and not showing a decreasing trend over time), doses of up to 40 mg/kg may be considered.
- Doses above 40 mg/kg are not recommended.
- If the serum ferritin falls consistently below 500 mcg/L consider temporanly interrupting therapy.
Based on Serum Creatinine
- For adults, reduce the daily dose of DESIROX by 10 mg/kg if a rise in serum creatinine to >33% above the average of the pretreatment measurements is seen at 2 consecutive visits, and cannot be attributed to other causes.
- For pediatric patients, reduce the dose by 10 mg/kg if serum creatinine levels rise above the age-appropriate upper limit of normal at 2 consecutive visits.
Concomitant UGT Inducers or Cholestyramine
- Concomitant use of UGT inducers or cholestyramine decreases deferasirox systemic exposure (AUC) Avoid the concomitant use of cholestyramine or potent UGT inducers (e g . rifampicin, phenytoin. phenobarbital, ritonavir) with DESIROX.
- If you must co-administer these agents together, consider increasing the initial dose of DESIROX to 30 mg/kg, and monitor serum ferritin levels and clinical responses for further dose modification
Hepatic Impairment
- Avoid the use of DESIROX in patients with severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment
- Reduce the starting dose by 50% in patients with moderate (Child-Pugh B) hepatic impairment.
- Closely monitor patients with mild (Child-Pugh A) or moderate (Child-Pugh B) hepatic impairment for efficacy and adverse reactions that may require dose titration.
How to Administer Desirox
- Take once daily on an empty stomach, at least 30 minutes before food, preferably at the same time each day.
- Doses (mg/kg per day) should be calculated to the nearest whole tablet Tablets should not be chewed or swallowed whole.
- Tablets should be completely dispersed by stirring in water, orange juice, or apple juice until a fine suspension is obtained.
- After swallowing the suspension, any residue should be resuspended in a small volume of liquid and swallowed.
- Doses of <1 g should be dispersed In about 100 ml (3.5 ounces) of liquid and doses of> 1 g in about 200 ml (7.0 ounces) of liquid.
- DESIROX should not be taken with aluminum-containing antacid products.
Monitoring Guidelines
Contraindications
DESIROX is contraindicated in patients with:
- Creatinine clearance <40 mL/mm or serum creatinine>2 times the age-appropriate upper limit of normal
- Poor performance status and high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes or advanced malignancies
- Platelet counts <50 x 109-/L
- Known hypersensitivity to deferasirox or any component of DESIROX
Related Topics

.svg?iar=0&updated=20230109065058&hash=B8F025B8AA9A24E727DBB30EAED272C8)