Budesonide?Formoterol More Effective than SABA Alone in Mild Asthmatic Patients
22 Oct, 18
Aim
To compare the safety and efficacy of budesonide/formoterol as needed to (short-acting ?2 –agonists (SABA) as needed to budesonide maintenance therapy plus SABA as needed.
Patient Profile
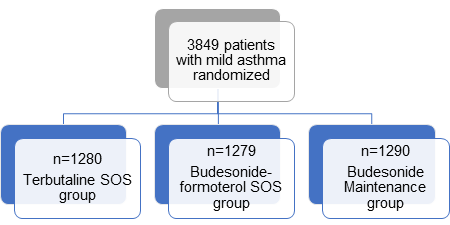
- N= 3849
- Patients ≥12 years of age
- Documented diagnosis of asthma as per Global Initiative for Asthma [GINA] 2012 criteria for at least 6 months prior
- Patients who need step 2 treatment according to Global Initiative for Asthma guidelines for at least 30 days before run-in period
Study Design
- Double-blind, randomized, parallel-group, 52-week, phase 3 trial
Treatment
- Terbutaline group: Twice-daily placebo plus terbutaline (0.5 mg, used on an as-needed basis)
- Budesonide-formoterol group: Twice-daily placebo plus budesonide– formoterol (200 ?g of budesonide and 6 ?g of formoterol, used on an as-needed basis)
- Budesonide maintenance group: Twice-daily budesonide (200 ?g) plus terbutaline (0.5 mg, used on an as-needed basis)
- Duration: 52 week
Endpoints
Primary Endpoint
- To show that budesonide–formoterol used as needed was superior to terbutaline used as needed in terms of asthma symptom control, measured according to the electronically recorded weeks with well-controlled asthma
Secondary Endpoints
- Non inferiority of study treatment ie formoterol-budesonide as-needed vs budesonide maintenance treatment in terms of asthma control
- Time to the first severe exacerbation (defined as worsening asthma leading to the use of systemic glucocorticoids for ≥3 days, inpatient hospitalization, or an emergency department visit leading to the use of systemic glucocorticoids)
- The rates and time to the first moderate-to-severe exacerbation (including worsening asthma requiring the addition of inhaled budesonide at a dose of 200 ?g twice daily to avoid progression to a severe exacerbation) in the budesonide-formoterol group versus the terbutaline group and versus the budesonide maintenance group
- Asthma Control Questionnaire–5 (ACQ-5) scores,
- Lung function variables
- Quality of life (according to the Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire [AQLQ] score)
- Safety was evaluated according to the type, incidence, and severity of adverse events and by monitoring of vital signs
Results
- The final analysis included data from 3836 patients
- 3363 patients (87.4%) completed the trial
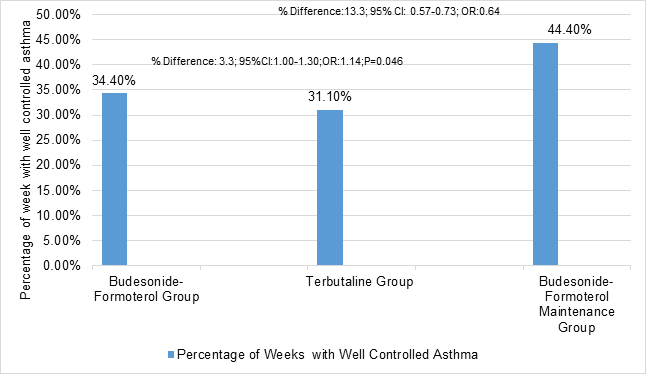
- Budesonide-formoterol was superior to terbutaline but inferior to budesonide maintenance therapy as assessed by electronically recorded weeks with well-controlled asthma per patient
Figure 1: Mean percentage of electronically recorded weeks with well-controlled asthma with three groups
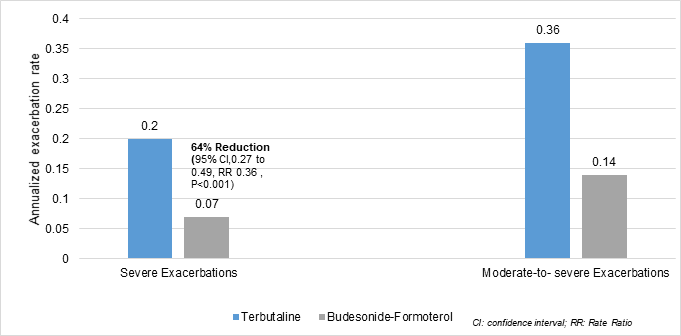
- Budesonide-formoterol used as needed prolonged the time to the first severe exacerbation, as compared with terbutaline used as needed (hazard ratio, 0.44)
Figure 2: Reduction in rates of severe and moderate to severe exacerbations
- No significant difference in adherence was observed between groups
- Rate of adherence in budesonide maintenance group was (78.9%); terbutaline group (79.0%); budesonide –formoterol group (79.1%)
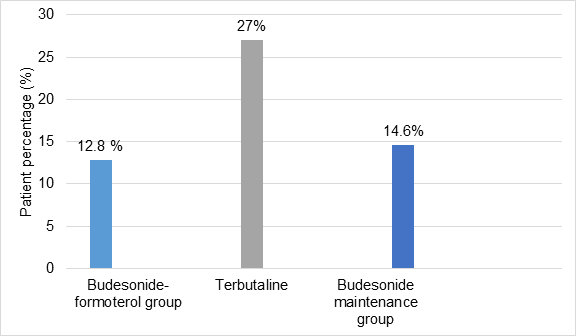
- Fewer patients in budesonide-formoterol group were prescribed inhaled or systemic glucocorticoids for asthma than in terbutaline or budesonide maintenance group
Figure 3: Prescription of inhaled systemic glucocorticoids for asthma between groups
- The median metered daily dose of inhaled glucocorticoid in the budesonide-formoterol group (57?g) was 17% of the dose in the budesonide maintenance group (340?g)
Conclusion
- Budesonide–formoterol used as needed resulted in
- 64% lower rate of severe exacerbations than terbutaline used as needed
- 60% lower rate of moderate-to-severe exacerbations than terbutaline used as needed
- Budesonide-formoterol was superior to terbutaline but inferior to budesonide maintenance therapy in terms of in terms of electronically recorded weeks with well-controlled asthma
- Budesonide-formoterol group (34.4%)
- Terbutaline group (31.10%)
- Budesonide –formoterol Maintenance group (44.4%)
The budesonide /formoterol treatment was as effective as budesonide maintenance group with less than 1/5th the dose of inhaled corticosteroid used in the budesonide/formoterol group compared to the budesonide maintenance therapy
N Engl J Med 2018; 378:1865-76