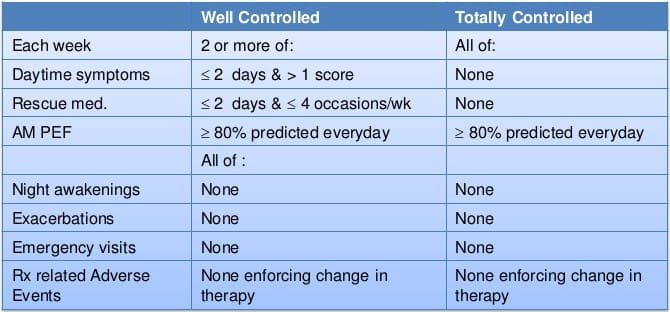
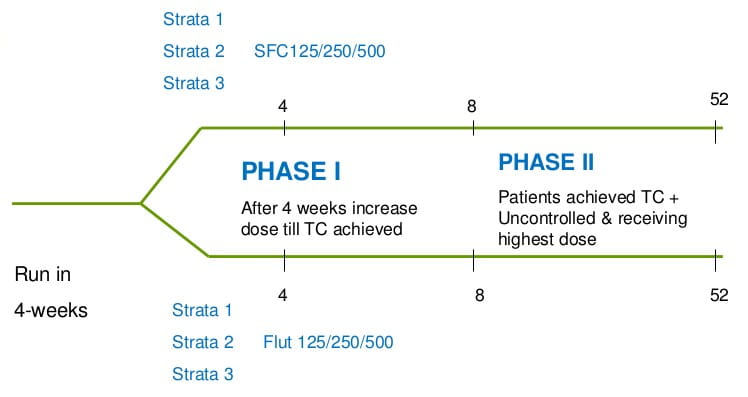
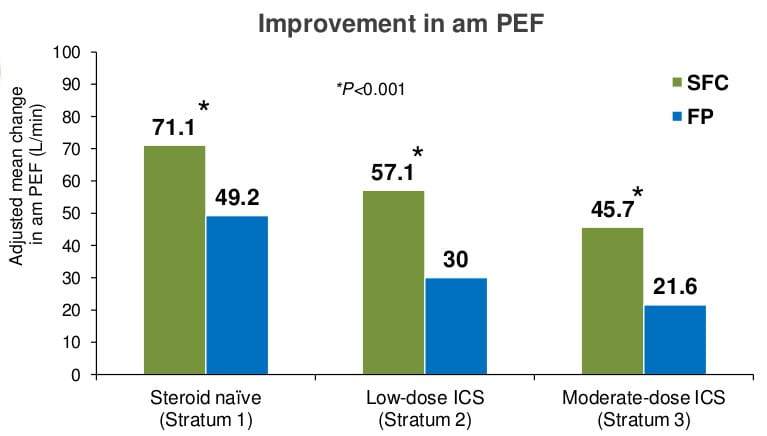
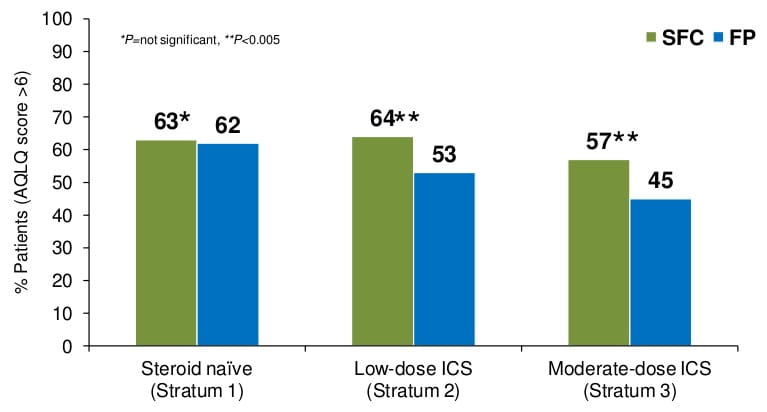
These patients were then randomized and stratified according to baseline treatment in previous 6 months.
Stratum 1. Corticosteroid na?ve or 'corticosteroid-free'
Stratum 2. <500 mcg BDP daily or equivalent
Stratum 3. >500 - <1000 mcg BDP or equivalent
Stratified, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group study
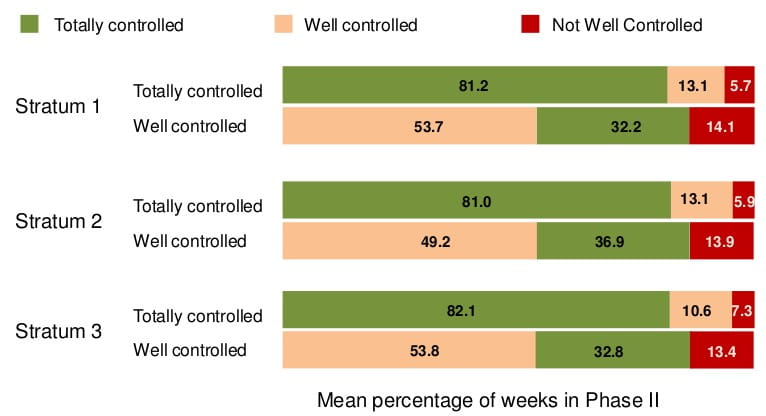
Patients achieving TC at any time during Phase I were placed into Phase II & continued with the same dose
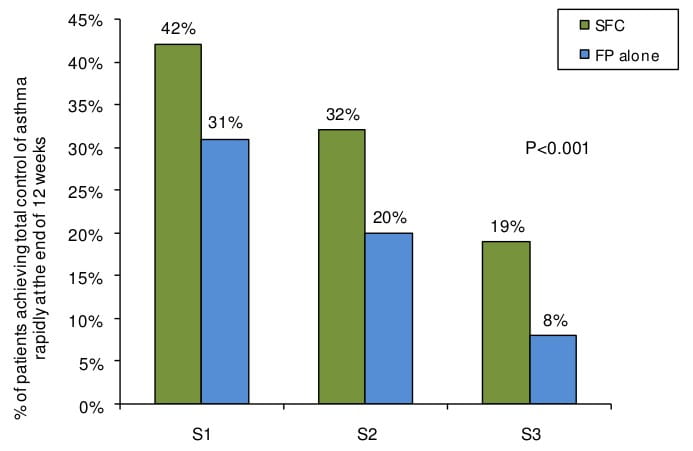
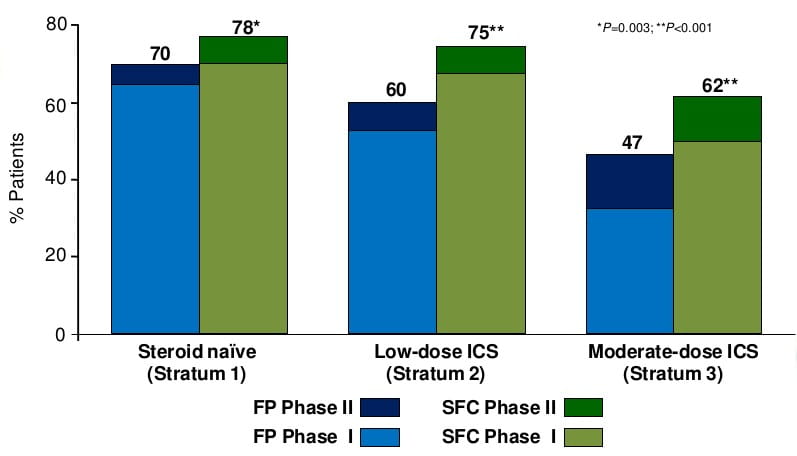
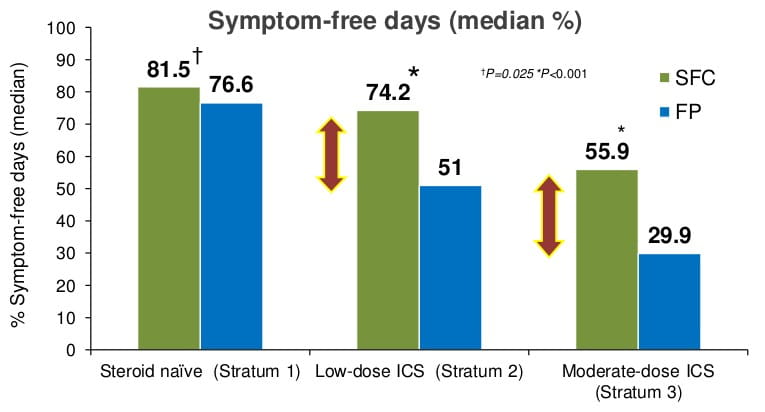
Difference represents an additional 85-95 symptom-free days per year with SFC in patients previously symptomatic on ICS