Montelukast Safe and Effective in Patients with Asthma and Allergic Rhinitis
Introduction
Comorbidity of asthma and allergic rhinitis (AR) has been well established, suggesting a link between upper and lower airway disease. A significant proportion of asthmatic patients have AR and vice versa, leading to high healthcare costs and worse quality of life (QoL). Blocking of cysteinyl leukotriene receptor might be beneficial in patients with both asthma and AR. Recent clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of montelukast, a leukotriene antagonist, in adults with both asthma and AR.
Aim
This phase IV study evaluated the efficacy and safety of add-on montelukast 10 mg to existing controller medication in the treatment of patients with both asthma and AR in a real-life setting.
Methods
Study Design
- Multicenter, phase IV study
Patient Profile
- Patients with confirmed diagnosis of both asthma and AR
- Age >16 years
- Montelukast was given either as a monotherapy or an add-on to another anti-asthmatic therapy which was judged to be inappropriate prior to the administration of montelukast
Treatment Strategy
- The overall cohort comprised 5855 patients with a mean age of 42.8±15.4 years
- Demographics, disease severity, symptoms, need for rescue medication and inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) and QoL was recorded at baseline
- Efficacy and safety outcomes following treatment for 4-6 weeks was compared to baseline
Endpoints
- General improvement in asthma symptoms
- Improvement of day-time and night-time asthma symptoms
- Need for rescue medication or ICSs
- General and specific improvement in AR symptoms
- Reduction in AR medication use
- General and specific QoL improvement
- Undesirable effects (UEs)
- Adverse drug effects (ADE)
Results
- Baseline characteristics of cohort were as follows:
- 40.5% had moderate asthma with both day-time and night-time symptoms
- The most frequently reported symptom was cough
- 51.8% and 47% had intermittent and persistent AR respectively
- Overall QoL was reduced in 70%
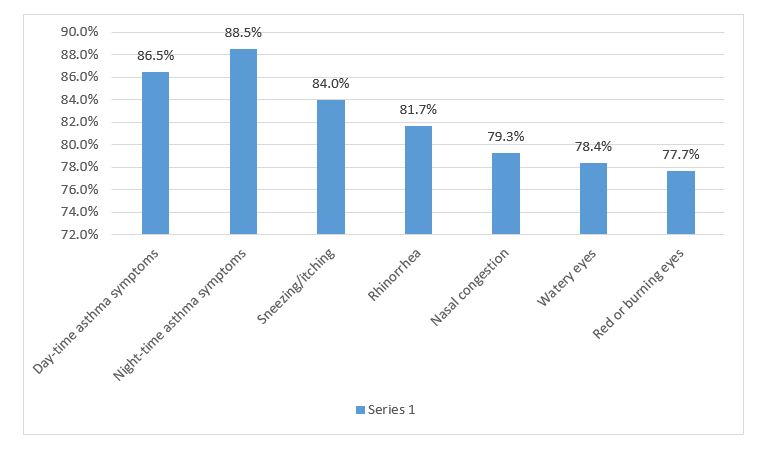
- A significant improvement in all the efficacy parameters was reported following treatment with montelukast as seen in Figure 1.
- The use of asthma and rhinitis medication was also reduced post treatment with montelukast
- A high proportion of patients (92.3%) intended to continue montelukast therapy.
- There was a marked improvement in overall QoL and 85.2% reported QoL as “very good” or “good”
- A “strong” or “marked” improvement in each of the four domains of sleep, work, everyday life and physical activity was reported in 86.3%, 81.6%, 84.4% and 82.1% respectively.
- Montelukast was well tolerated with the incidence of adverse drug reactions in 14 out of 6158 patients.
- There were no serious adverse events.
Conclusion
- Montelukast 10 mg is a safe and effective systemic treatment of both upper and lower airways in patients with both asthma and allergic rhinitis in a real-life setting.
Respir Med. 2006 Nov;100(11):1952-9. Doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2006.02.026.