Non-inferiority of Avanafil to Sildenafil in Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction
17 Jun, 22
Introduction
The efficacy of various phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors has been established in the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED). However, a number of patients either fail to respond clinically to PDE5 treatment or discontinue the treatment due to adverse events (AEs). Avanafil is a second generation, selective PDE5 inhibitor, with a rapid onset of action. There is lack of evidence on the comparison of efficacy and safety of avanafil with other PDE5 inhibitors.
Aim
This study compares the efficacy and safety of avanafil with sildenafil in the management of Indian patients with ED.
Method
Study Design
- Prospective, randomized, double-blind, two-arm, active-controlled, parallel, multicenter, non-inferiority clinical study.
Treatment Strategy
- The study population comprised patients aged >21 years with a history of ED for at least 3 months and International Index of Erectile Function - Erectile Function (IIEF-EF) domain score of <26.
- The patients were randomized to receive avanafil or sildenafil in 1:1 ratio.
- the patients were initially given 100 mg avanafil tablets or 50 mg sildenafil tablets for 4 weeks.
- The dose was increased to avanafil 200 mg or sildenafil 100 mg if required after 4 weeks.
- The patients were followed by for a duration of 12 weeks with scheduled visits after every 4 weeks.
Endpoints
- IIEF-EF score
- AEs
Results
- A total of 111 were assigned to avanafil group and 109 to sildenafil group.
- Dose escalation was required in 40% of patients in the avanafil group and 45.6% of patients in the sildenafil group at 4 weeks of treatment.
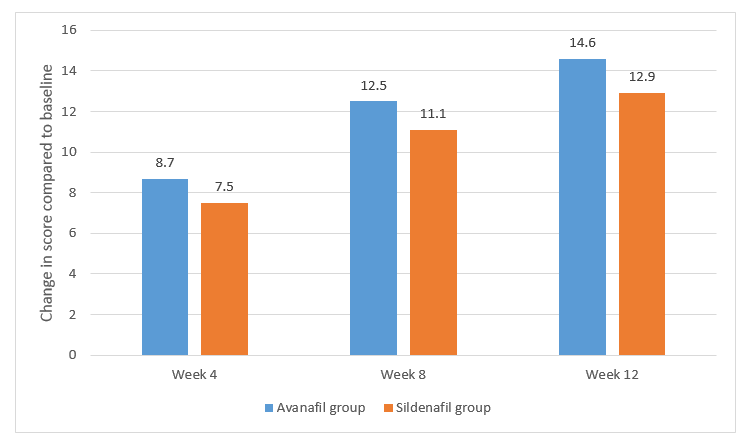
- The difference in the mean change of IIEF-EF score from baseline in the two groups increased from week 4 to week 8 and week 12, demonstrating non-inferiority at week 4, and superiority at week 8 and week 12 as seen in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Change in IIEF-EF domain score
- Avanafil group showed a significantly better response to modified Sexual Encounter Profile 1 (84.8% vs 28.2%) in the sildenafil group; indicating a rapid onset of action; p<0.001.
- Both the drugs were well tolerated by all the patients.
- All the AEs were mild, and none were serious or required discontinuation of treatment.
- The most common AE reported was headache in both the groups.
Conclusion
- The results of the study revealed that avanafil was superior to sildenafil in improving the International Index of Erectile Function - Erectile Function domain score at the end of 12 weeks of treatment.
- Avanafil demonstrated noninferiority/superiority in other efficacy parameters compared to sildenafil.
- Avanafil was associated with rapid onset of action leading to better clinical response.
Int J Urol. 2022 Apr;29(4):351-359. Doi: 10.1111/iju.14785.