Topical Cyclosporine 0.05% and Osmoprotective Lubricating Eye Drops: Role in the Management of DED and Inflammation
24 Dec, 21
Introduction
Reduced aqueous production seen in aqueous?deficient dry eye disease (DED) and/or increased evaporation seen in the evaporative DED may result in tear film hyperosmolarity. Evaporative DED is encountered frequently in clinical practice, though there is a substantial overlap between aqueous?deficient and evaporative DED. Various inflammatory markers including; interleukin-1? (IL-1?), IL-6, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), etc. have also been associated with DED. Controlling inflammation has a key role in improving the ocular surface health in DED.
Aim
To evaluate the effect of topical cyclosporine 0.05% and osmoprotective lubricating eye drops in patients with DED with inflammation
Patient Profile
- Patients with mild to moderate aqueous deficiency and evaporative dry eye with two or more of the following criteria:
- Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI) >12
- Tear break up time (TBUT): 6-10 s
- Schirmer’s test I result: 8–10 mm/5 min
- Ocular surface staining
Methods
Study Design
- An open-label prospective study
Assessment
- Ocular surface inflammation was assessed by evaluating MMP?9 positivity from tears of the study participants
Treatment Strategy
- Patients were prescribed osmoprotective lubricating eye drops four times a day and cyclosporine A 0.05% eye drops twice a day for 6 months.
Efficacy Outcomes
- Change in OSDI scores, Schirmer’s test and TBUT
- Reduction in ocular surface staining
- Reduction in MMP?9 levels
Results
- Patients with MMP?9 positivity had a significantly higher OSDI score (mean OSDI score 29.7, P=0.0052) and significantly decreased Schirmer’s test values (P=0.0013).
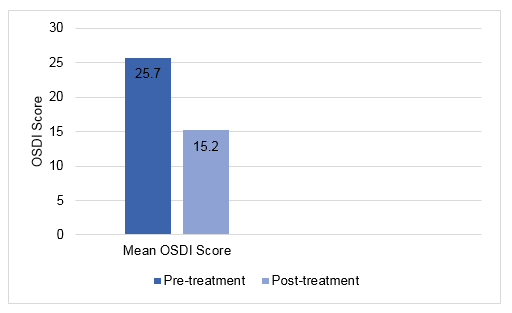
- Six months topical treatment was associated with a significantly improved OSDI scores (mean pre-treatment: 25.7, and mean post-treatment: 15.2, P <0.001) (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1: Change in OSDI score during the study
- The proportion of patients who were MMP?9 positive reduced substantially. Of the 75 eyes that tested MMP?9 positive, 70.66% showed significant reduction in MMP?9 levels post-treatment (P < 0.0001).
- During the pre-treatment period, 35.85% eyes (n=38 eyes) exhibited corneal staining, the same reduced significantly to 18.87% (n=20 eyes) after 6 months of treatment. TBUT improved from 7.67 to 8.15 s (p=0.06). There was no statistically significant difference in pre-and post-treatment Schirmer’s test results.
Conclusions
- Six-month treatment with topical osmoprotective lubricating eye drops and cyclosporine A 0.05% reduced inflammation in patients with DED, as measured by levels of tear MMP?9.
- Reduction in inflammation correlated with improved OSDI scores and ocular surface staining.
- Topical cyclosporine A 0.05% and osmoprotective lubricants have an important role in the management of DED.
Indian J Ophthalmol 2021;69:3473-7.
Related Topics