Management of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) has changed dramatically over years and there has been gradual shift from use of surgical therapy to medical therapy. Medical treatment includes use of an ?-blocker and/or 5 ?-reductase inhibitor. A fast and sustained improvement of bothersome urinary symptoms, maximum flow rate and quality of life are considered to be important short-term treatment goals in lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of BPH. However, it is increasingly recognized that BPH is slowly progressing disease. Hence halting progression of disease and thus reducing occurrence of serious complications such as acute urinary retention (AUR) and need for surgery have become major treatment goals.
Alpha-blockers offer rapid symptomatic relief. However, alpha-blockers lack any effect on prostate volume. 5 alpha-reductase inhibitors (5-ARI) inhibit 5 alpha-reductase enzyme which is responsible for conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is an androgen primarily responsible for enlargement of prostate gland. Thus 5 alpha-reductase inhibitors reduce prostate size there by halting disease progression. However, symptomatic relief with 5ARIs may be delayed for 3-6 months. Combination of an alpha-blocker and 5 alpha-reductase inhibitor thus combines benefits of individual monotherapy and provides rapid symptomatic relief as well as reduces the risk of progression.
It was in 2003, that the landmark trial -Medical Therapy of Prostatic Symptoms- (MTOPS) showed for the first time that percentage reduction in overall risk of BPH progression was significantly greater with combination therapy than either monotherapy. Although MTOPS study contributed substantially to the understanding of the role of combination therapy for symptomatic BPH, some of the issues still remain unresolved. In MTOPS study, only a subset of patients was at heightened risk for progression. Also MTOPS study used finasteride as 5-ARI which blocks only type II 5 alpha reductase enzyme.
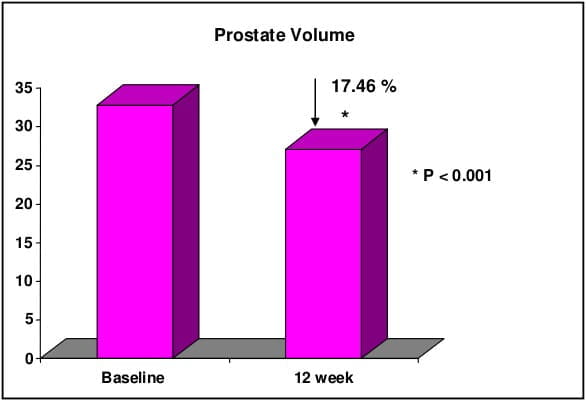
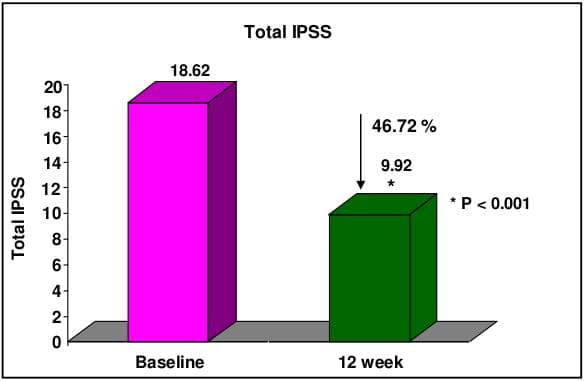
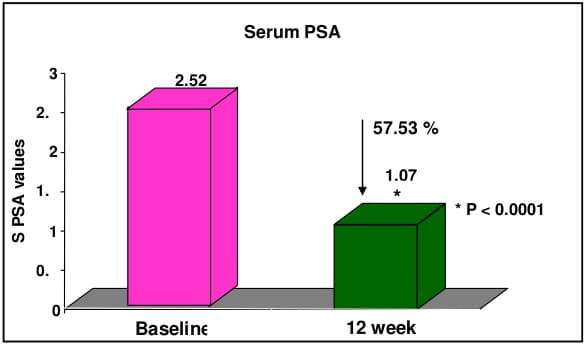
CombAT, combination of Avodart and Tamsulosin was the first long-term study which assessed the benefits of combination of tamsulodin and dutasteride over monotherapy in men who are at risk of progression by virtue of having prostate volume ≥30 cm3 and PSA ≥1.5 ng/ml. Tamsulosin hydrochloride is a subtype selective ?1A-blocker which has 15 fold higher selectivity for ?1A subtype than ?1B subtype of adrenoreceptors. Higher ?1A selectivity reduces the propensity for vasodilatory side effects. Dutasteride is a 5 ARI which blocks both type I and type II 5 alpha-reductase enzyme, whereas finasteride blocks only type II 5 alpha-reductase enzyme. Thus, treatment with dutasteride results in greater degree and consistency of dihydrotestosterone suppression compared with finasteride.
CombAT provides support for long-term use of dutasteride and tamsulosin combination therapy in men with moderate to severe LUTS due to BPH and prostatic enlargement at increased risk of progression.
Based on CombAT study results, fixed dose combination of tamsulosin and dutasteride was approved by US FDA.