Higher Ovulation Rates with Combination Therapy of Letrozole and Clomiphene Citrate in Women with PCOS
4 Aug, 20
Introduction
The treatment of infertility in patients with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) focuses on ovulation induction. Clomiphene citrate (CC), works as a selective estrogen receptor modulator by competitively attaching to nuclear estrogen receptors. Letrozole is another commonly used oral ovulation induction agent, which works as a highly selective aromatase inhibitor, preventing androgen-to-estrogen conversion. Combination of both these drugs might improve ovulatory rate as compared to letrozole alone. However, the impact of both the drugs on the ovulatory rate has not been studied in a prospective randomized fashion.
Aim
The efficacy of combination of letrozole and CC was compared to letrozole alone in PCOS women.
Method
Study Design
- Open-label, randomized controlled trial
Treatment Strategy
- Women 18–40 years of age with a diagnosis of infertility and PCOS as defined by the Rotterdam criteria and no other known cause of infertility were included.
- Participants were randomized in a 1:1 ratio, to either 2.5 mg letrozole alone or the combination of 2.5 mg letrozole and 50 mg CC daily on cycle days 3–7 for one treatment cycle.
- A mid-cycle ultrasound was performed on day 12-14
- In case the results of an ovulation prediction kit (OPK) were positive, serum progesterone was measured after 7 days
- Results were analysed according to the intention-to-treat principle.
Primary End Points
- Ovulation, defined as a mid-luteal progesterone level >3 ng/mL, tested 7 days after a positive OPK test or on cycle day 21 if no surge was detected
Secondary End Points
- Conception
- Clinical pregnancy
- Live birth
- Singleton birth
- Pregnancy loss
- Size and number of developing follicles and endometrial thickness on cycle day 12–14 ultrasound
- Adverse events
Results
- A total of 70 PCOS women were randomized to the 2 groups of 35 each receiving either letrozole alone or combination of letrozole and CC
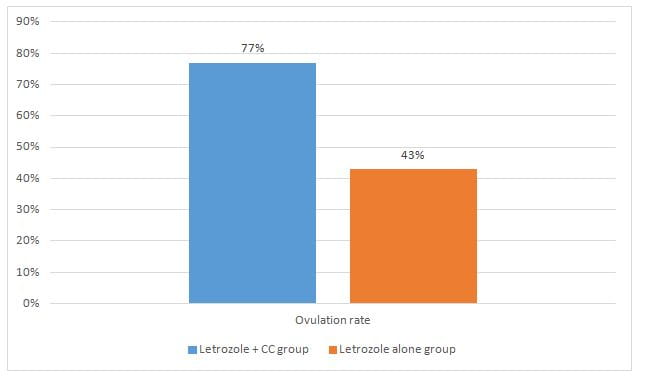
- The ovulation rate of the combination group was significantly higher as compared to letrozole-alone as seen in figure 1.
Figure 1. Comparison of ovulation rate
- The differences in conception, pregnancy, and live birth between the two groups were not significant
- Among the participants who ovulated, there was no significant difference in endometrial thickness, median number of follicles >15 mm, largest follicle size, or serum progesterone level
- No serious adverse events were reported in either group; the side-effects profile was similar in both the groups
- Headache (41%), fatigue (22%), and abdominal pain or cramping (19%) were the most common side effects in the letrozole group
- The combination group reported hot flashes (31%), headache (28%), and abdominal pain or cramping (19%) as the most common side effects
Conclusion
- Combination of letrozole and clomiphene citrate (CC) was associated with significantly higher ovulation rates than letrozole alone in women with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS).
- Combination therapy may be an alternate low-risk, low-cost infertility treatment with superior ovulation rates.
- Additional randomized clinical trials are warranted to evaluate the pregnancy and live birth rates.
Fertil Steril 2019;111(3):571-8.