Rizatriptan vs. Ibuprofen for the Treatment of Acute Migraine
25 Jan, 22
Introduction
Rizatriptan is reported to be more effective than other triptans and ergotamine and caffeine combination in relieving acute migraine attacks. Rizatriptan has not been compared with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in migraine patients.
Aim
To compare the efficacy of rizatriptan and ibuprofen in migraine patients
Patient Profile
- Migraine patients aged >12 years and having <8 attacks/month (n=155)
Method
Study Design
- A randomised placebo-controlled trial
Treatment Strategy
- Patients were randomised to rizatriptan 10 mg (n=53), ibuprofen 400 mg (n=52) or placebo (n=50).
Outcomes
Primary Outcome
- Percentage of patients having pain relief at 2 hours
Secondary Outcomes
- Percentage of patients with relief of associated symptoms, functional disability at 2 hours and pain freedom at 24 hours
Results
- Mean age of the study population was 30.5 years and 106 of them were females. All patients had migraine without aura. Mean frequency of migraine attacks per month was 4.4 years.
- The mean headache score was 2.44, associated symptoms score 2.08 and functional disability score 2.36.
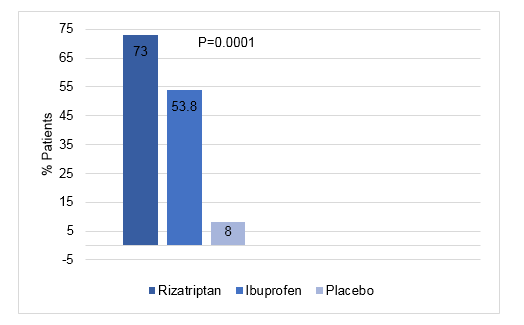
- Significantly higher proportion of patients treated with rizatriptan vs. ibuprofen or placebo experienced a 2-hour headache relief (Fig. 1)
Fig 1: Patients with 2-hour headache relief during the study
- Rizatriptan was better than ibuprofen and placebo in achieving headache freedom at 2 hours (rizatriptan; 37.7%, ibuprofen; 30.8%, placebo 2%).
- Rizatriptan was superior to ibuprofen and placebo in relieving headache at 2 hours but not at 24 hours.
- Patients treated with rizatriptan experienced significant relief in associated symptoms and functional disability and insignificant improvement in headache score vs. ibuprofen.
- Significantly higher proportion of patients treated with ibuprofen vs. rizatriptan required rescue medication (p=0.04).
- The incidence of adverse effects did not differ much between rizatriptan- and ibuprofen-treated patients (rizatriptan; 9, ibuprofen; 8, placebo; 3).
Conclusions
- Rizatriptan and ibuprofen were superior to placebo in aborting acute migraine attack.
- Rizatriptan 10 mg was superior to ibuprofen in relieving headache, associated symptoms and functional disability.
J Headache Pain. 2007; 8:175–179.