To compare the effects of telmisartan/hydrochlorothiazide (T/HCTZ) versus valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide (V/HCTZ) on early morning blood pressure (BP) in obese hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes.
SMOOTH
Title
Telmisartan/hydrochlorothiazide more effective than valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide in overweight/obese patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes.
Aim
Study Design
Prospective, randomized, open-label, blinded-endpoint, multicentre trial
Study Patients
Obese patients with type 2 diabetes and mild-to-moderate hypertension (N = 840)
Study Groups
Telmisartan 80 mg (n = 428) vs valsartan 160 mg (n = 412) for first 4 weeks, following which hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg was added in all patients for further 6 weeks
Study Duration
10 weeks
Primary End-point
Change from baseline in mean ambulatory systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) during the last 6 hours of the 24-hour dosing interval
Results
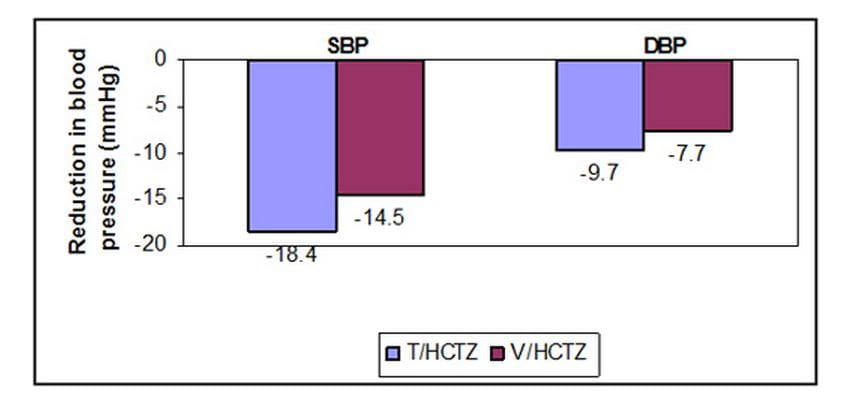
- T/HCTZ provided significantly greater reduction in BP in the last 6 hours of 24-hour dosing interval as compared to V/HCTZ
- T/HCTZ produced significantly greater reductions in 24-hour mean BP than V/HCTZ during the 24-hour dosing interval
- During the morning, daytime and night-time periods, patients receiving T/HCTZ had significantly greater reductions in mean ambulatory SBP & DBP vs those taking V/HCTZ
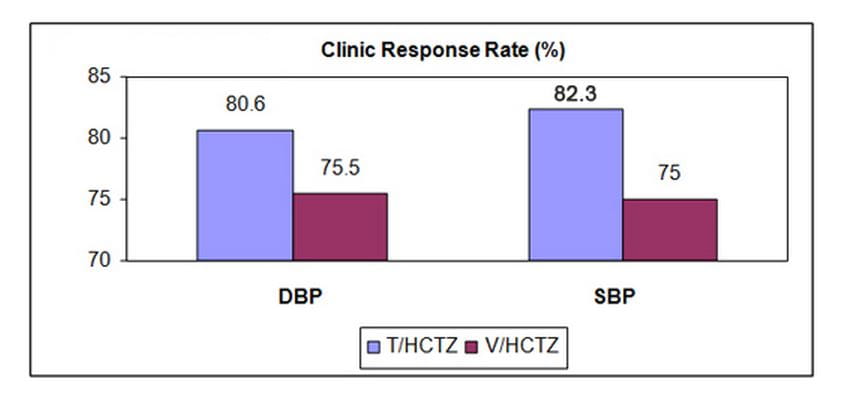
- Ambulatory as well as clinic DBP and SBP response rates were higher in patients taking T/HCTZ vs V/HCTZ
Safety
Both the treatments of T/HCTZ and V/HCTZ were well-tolerated and the overall incidence of adverse events was low.
Conclusion
- In high-risk, overweight/obese patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes, telmisartan/hydrochlorothiazide provides significantly greater BP lowering vs valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide throughout the 24-hour dosing interval, particularly during the hazardous early morning hours
-
The additional efficacy afforded by telmisartan/hydrochlorothiazide over valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide may confer a clinical advantage
Cardiovascular Diabetology 2007;6:28