Similar reductions in recurrent stroke and other vascular events with high-dose atorvastatin in men and women: Secondary analysis of the Stroke Prevention by Aggressive Reduction in Cholesterol Levels (SPARCL) study
SPARCL: Sub-analysis in Men & Women
Introduction
Aim
To compare the effects of atorvastatin 80 mg/day and placebo between men and women with recent stroke or TIA in the SPARCL study
Patients
Recent stroke or TIA and no known coronary heart disease (CHD) and LDL between 100 and 190 mg/dl (N=4731)
Study Groups
Atorvastatin 80 mg/day (n = 2,365) vs. placebo (n = 2,366)
Follow-up Period
6 years
Methods
Cox regression modeling to determine the effect of sex on the trial endpoints
Results
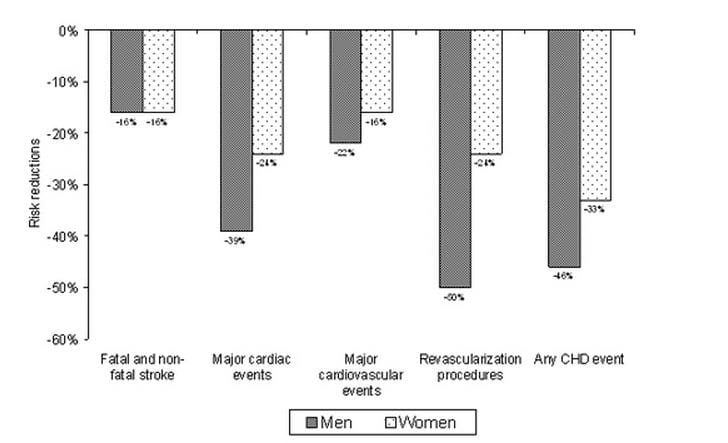
- Similar reductions in recurrent stroke as well as other cardiovascular events were seen with atorvastatin in men and women (Figure)
- Rates of treatment-related adverse events were low, and similar in both men and women
Conclusions
-
Stroke and other cardiovascular events are similarly reduced with atorvastatin 80 mg/day in men and women with recent stroke or TIA
Presented at 59th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, Boston, April 28- May 5, 2007. Presentation title "No Difference in Statin-Related Reductions in Recurrent Stroke or Other Vascular Events between Men and Women: Secondary Analysis of the Stroke Prevention by Aggressive Reduction in Cholesterol Levels (SPARCL) Study" Abstract no. S34.003