What is Cancer?
The body is made up of cells, which grow and die in a controlled way. Sometimes, cells keep on growing without control causing an abnormal growth called a tumor. A tumor can be benign (harmless), premalignant (if left untreated, may lead to cancer) or malignant (progressively worsens and can result in death). Cancer is a malignant tumor.
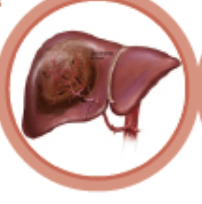
What is Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)?
When the main type of cells in the liver (hepatocyte) grows uncontrollably and forms a cancerous tumor, the disease is called malignant hepatoma or HCC (liver cancer).
What are the Possible Causes/Risk Factors of HCC?
In most cases, the causes/risk factors of HCC are as follows:
- Age: It is usually seen in people aged 50 years or older.
- Gender: It occurs more often in men than women.
- Alcohol tobacco and obesity are independent risk factors for the development of HCC, but, when combined, they appear to collectively increase the risk.
- Long-term (chronic) infection with hepatitis B (HBV) and hepatitis C (HCV) increases the risk.
- Cirrhosis (scar tissues in the liver) due to alcohol or too much iron in thelLiver (haemochromatosis) is one of the main risk factors for HCC.
- Aflatoxins from a fungus that can contaminate peanuts, wheat, soybeans, groundnuts, corn and rice can be a risk factor.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of HCC?
Many patients with HCC do not develop symptoms until the advanced stages of the tumor.
The symptoms of HCC may include any of the following:
- Nausea (feeling like vomiting)
- Unexplained weight Loss
- Bloating (feeling of fullness)
- Unexplained fever
- Tenderness (i.e. pain on applying pressure, particularly on the right-upper part of the abdomen [tummy])
- Swelling of the tummy
- Decreased appetite
- Swelling of the Legs
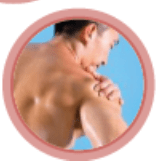
- Pain in the right shoulder
In case of the above symptoms, consult your doctor
How is HCC Diagnosed?
There are some general and some specific tests that need to be done to diagnose and confirm HCC, such as blood tests for tumor markers (substance in the body that may indicate the presence of cancer). If one has chronic hepatitis or known cirrhosis, a periodic screening with a Liver ultrasound or measurement of blood alpha-fetoprotein Levels may help detect HCC early. X-rays, CT scans, Liver scans, liver tissue biopsy {viewing under a microscope) etc., are some of the methods used for the diagnosis of HCC.
The doctor will decide the tests that are necessary; all of them may not be done.
How can HCC be Treated?
HCC is treatable upon early detection. Other treatments to relieve the symptoms improve the quality of the patient's life. The treatment depends on the type and stage and could include any therapy or a combination of therapies.
Various therapies are used for the treatment of cancer, e.g., removal of the tumor (surgery), killing cancer cells with drugs (chemotherapy) or radiation (radiotherapy).The doctor will decide on the treatment depending on the type and severity of the disease, and the condition of the patient.
How can HCC be Prevented?
Prevention is the best approach. The following protective measures may decrease the risk of HCC:
- Preventing and treating viral hepatitis early may help reduce the risk of HCC
- Eating a healthy, balanced diet with more fruits and vegetables
- Childhood vaccination against hepatitis B may reduce the hepatitis B disease and, thus, decreases the risk of HCC.
- Limiting alcohol consumption may help lower the risk of HCC
- Patients who develop progressive iron overload and cirrhosis may benefit from screening for increased iron level in the liver (hemochromatosis).
Do's and Don’ts
Do’s
- Periodic screening in the high-risk group
- Vaccination against hepatitis B
- Healthy diet
Don’ts
- Drink alcohol
- Use tobacco
- Eat processed foods
For more information, please consult your doctor.