Isoniazid Preventive Therapy in HIV Infection
14 Jul, 16
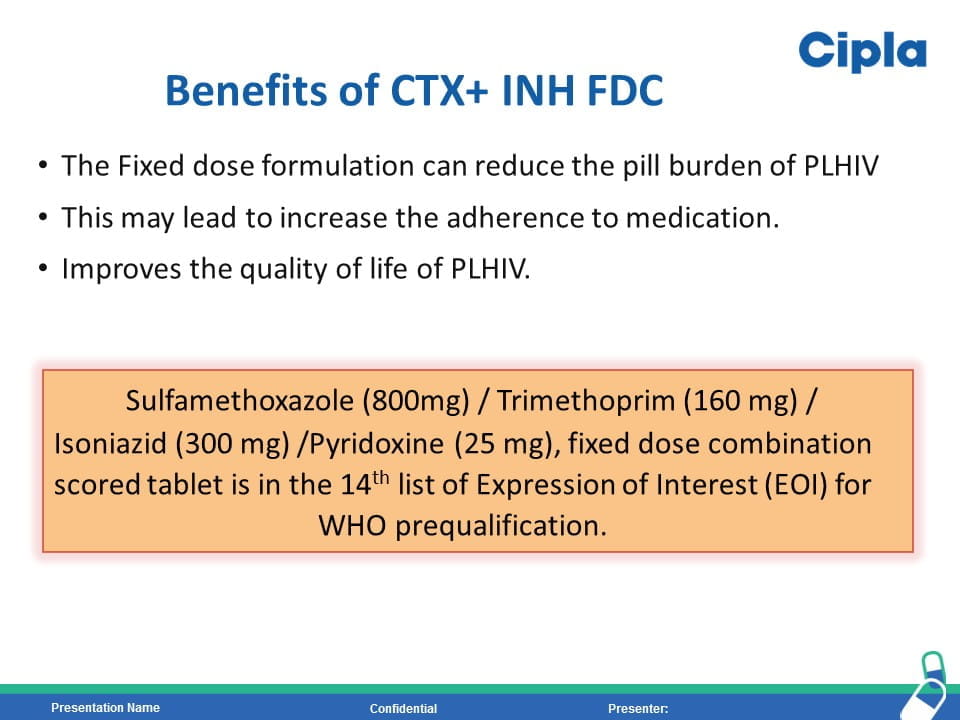
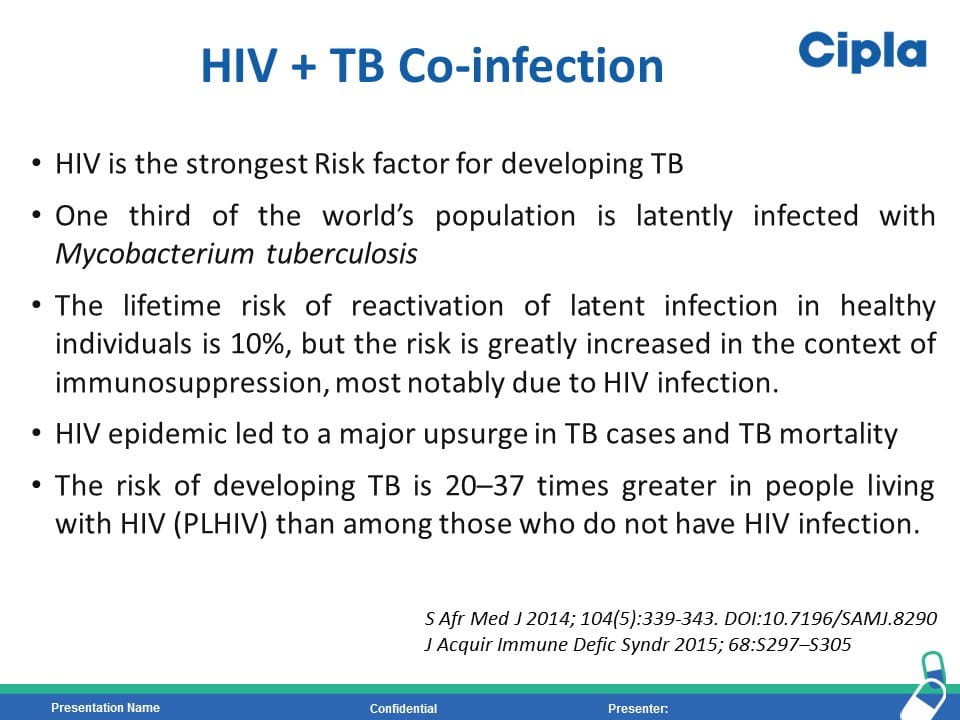
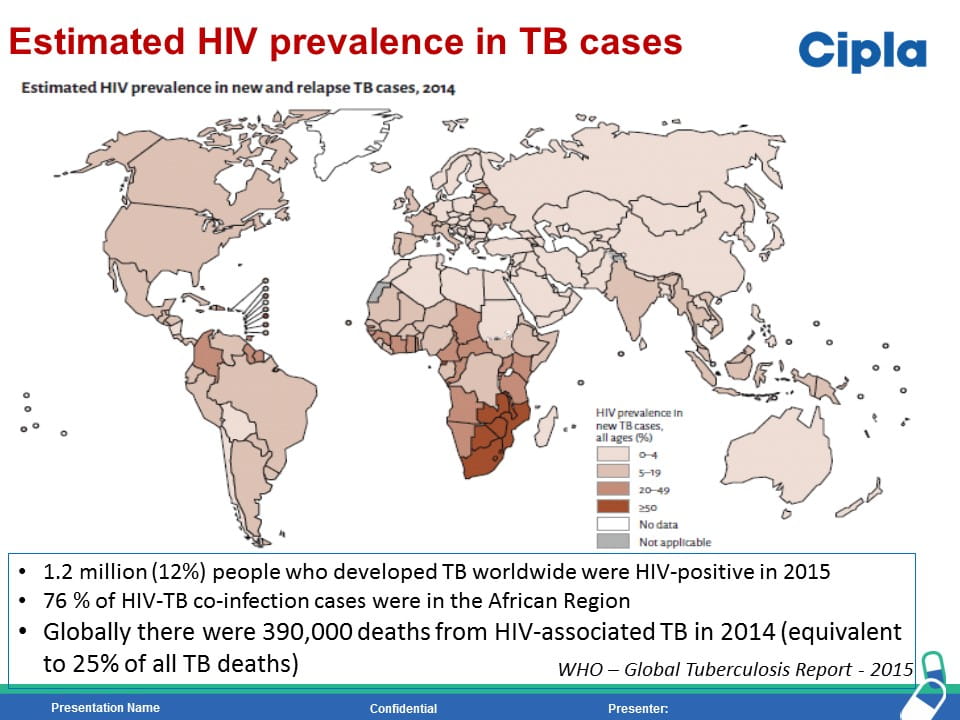
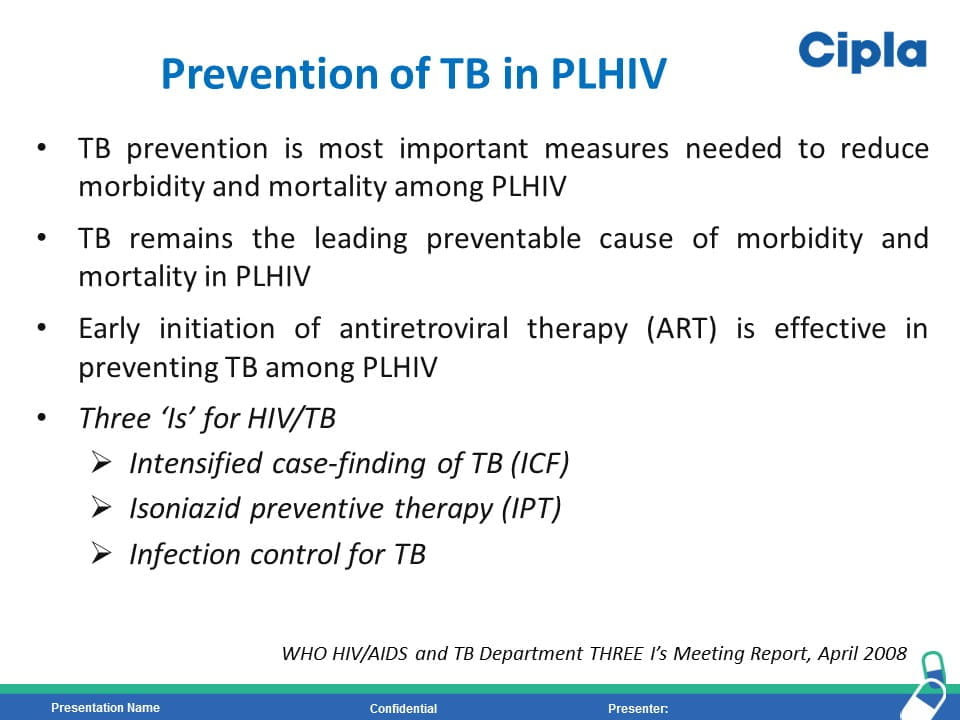
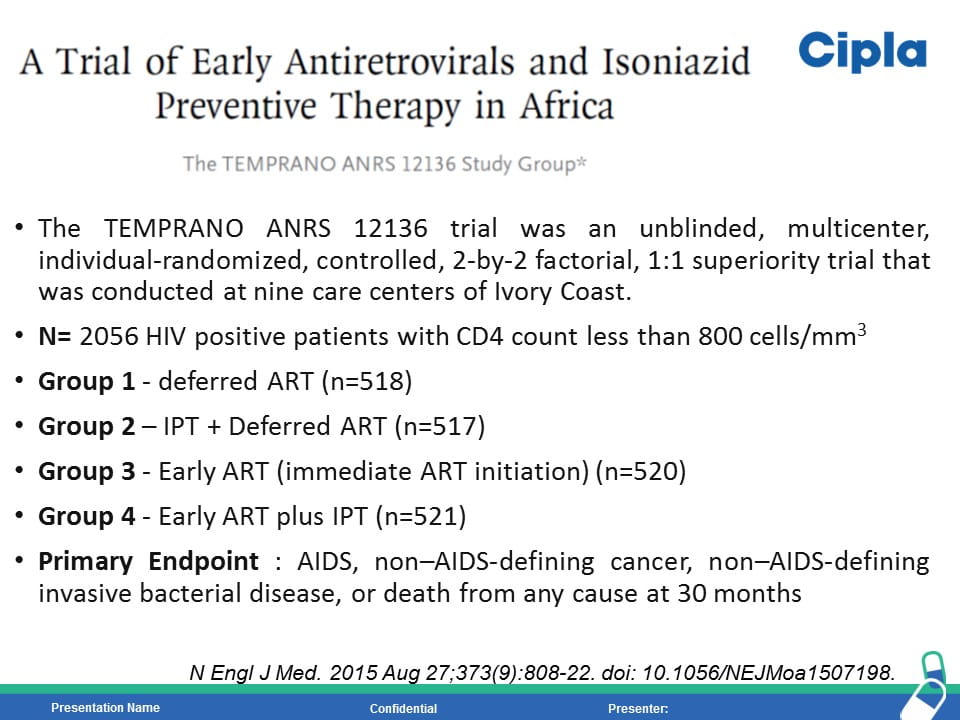
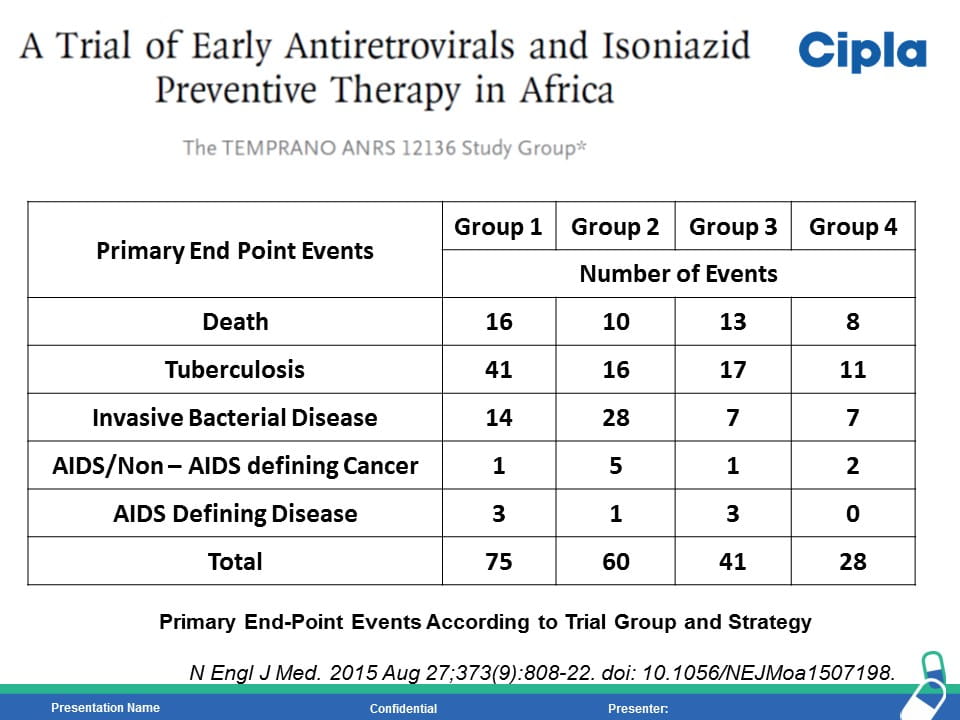
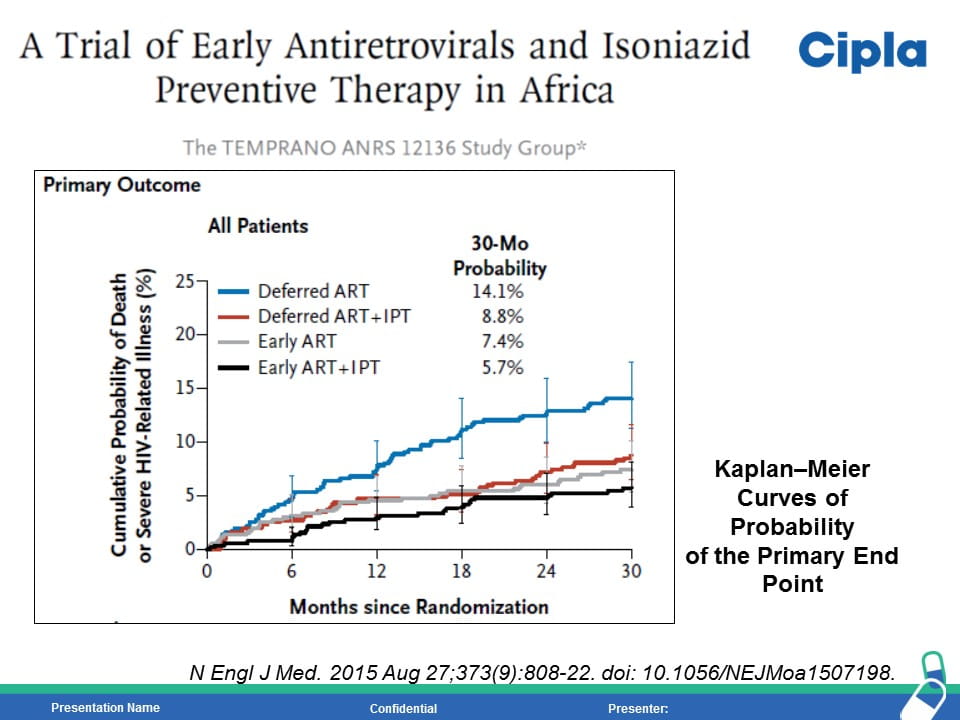
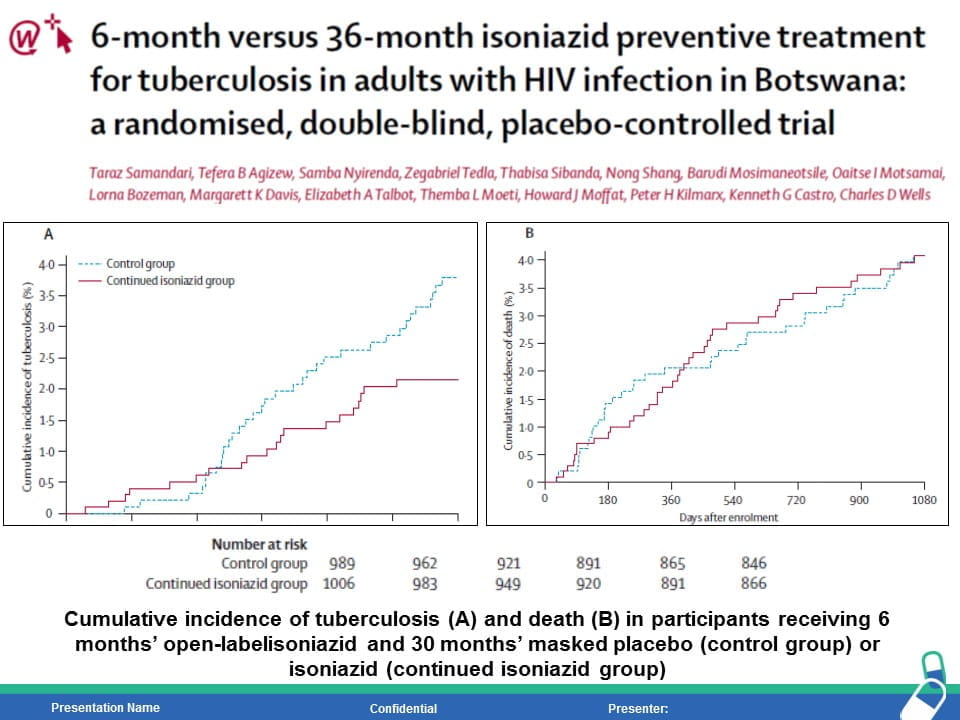
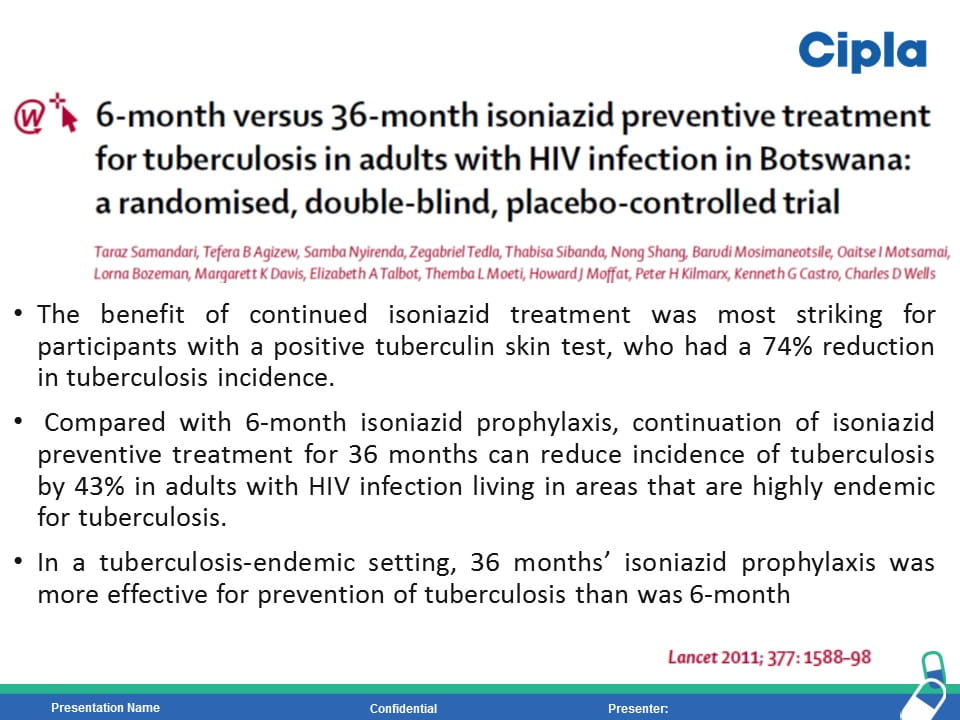
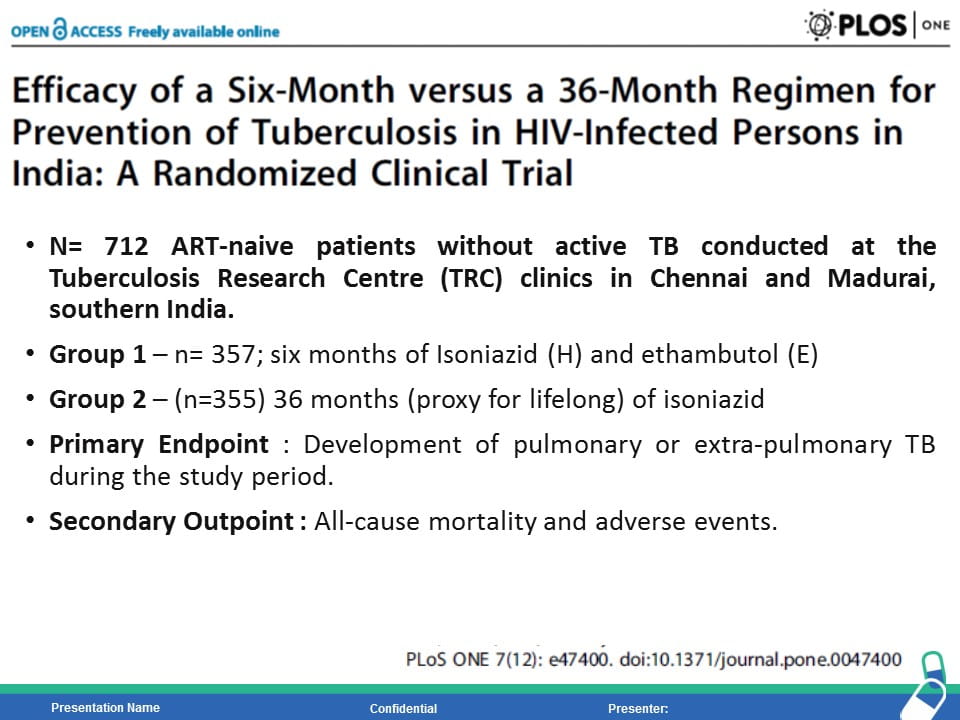
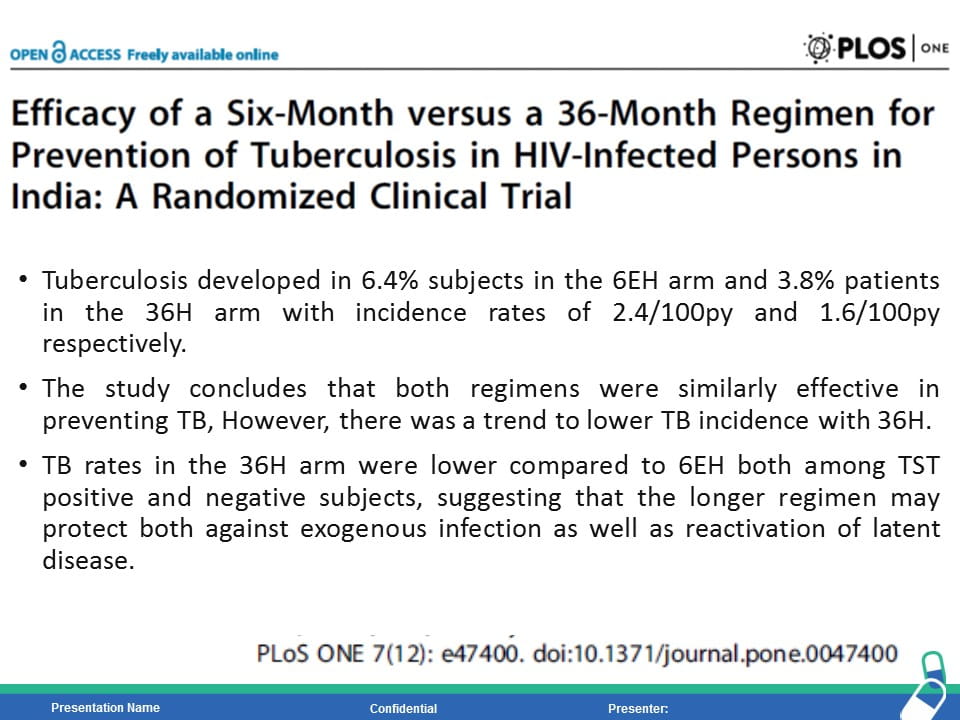
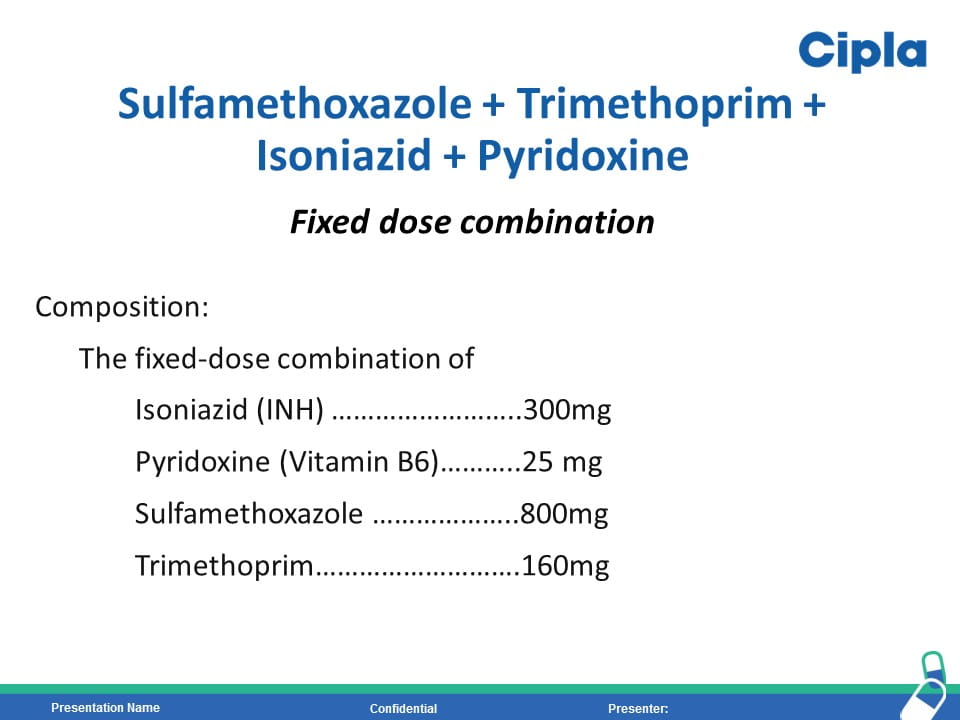
HIV is the strongest risk factor for developing tuberculosis (TB) disease in those with latent or new Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Prevention of TB is one of the most important measures needed to reduce morbidity and mortality among PLHIV. Isoniazid preventive therapy (IPT) has proved effective in reducing TB rates among HIV-infected patients. WHO recommends at least 36 months of isoniazid preventive therapy for adults and adolescents living with HIV, who have an unknown or positive tuberculin skin test status and among whom active TB disease has been safely ruled out. The fixed dose combination of Sulfamethoxazole (800mg) /Trimethoprim (160 mg) /Isoniazid (300 mg) /Pyridoxine (25 mg) can provide the overall protection from all the opportunistic infection including TB.
Related Slideshows